Setting up Windows Server 2003: 6. Shared folders access.
In the previous part of my Windows Server 2003 tutorial (Windows Server 2003: File sharing configuration), I describe how to set up four shared folders, called "Downloads", "Aly", "Ali", and "All Users", as well as how to configure the share permissions and NTFS rights of these folders for the 3 domain users "Admin", "Aly", and "Ali". In this part, we will see how to connect to these shares in order to read and write files from resp. to the server. The client machines used are "wk-winxpm" (a Windows XP Multimedia Edition workstation, supposed to be run by "Aly") and "wk-win2k" (a Windows 2000 Professional workstation supposed to be run by "Ali"). For an overview of the network, and the preceding parts of the tutorial, have a look at the first part of the tutorial Windows Server 2003: Introduction.
Accessing the shares from Windows XP.
One way to access the shared folders on Windows Server 2003 from Windows XP is to search Active Directory. To do so, open My Computer > My Network Places, and in the left pane click the link Search Active Directory. In the opening window, select Shared Folders from the "Find" combobox, then push the Find Now button. The four folders should now be listed in the bottom pane.
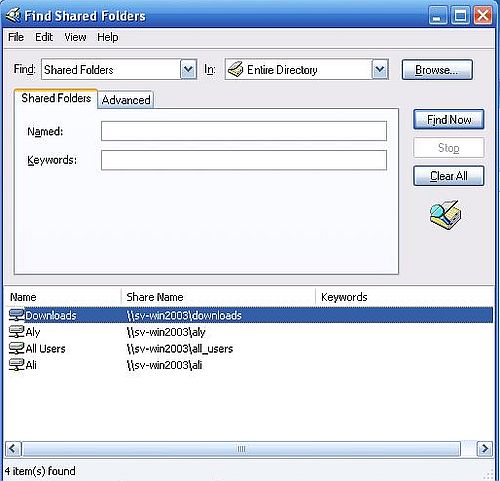 |
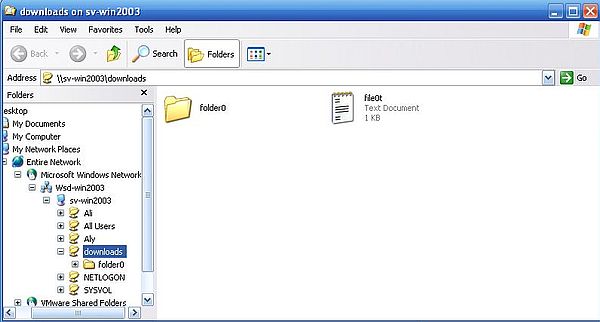
Double-clicking one of the items in the shared folders list should open the folder on the server in File Explorer. The screenshot shows how I opened the "Downloads" folder. The folder content, that you see on the screenshot, are a file and a subfolder, that I saved there on the Windows Server 2003 machine itself.
 |
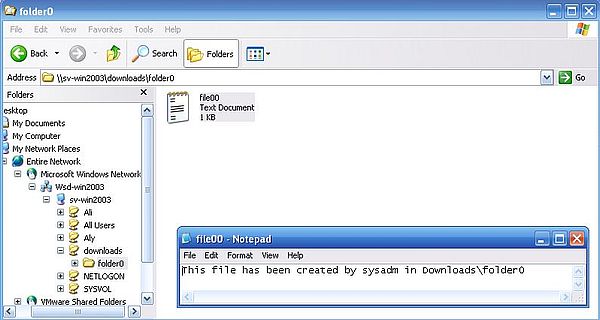
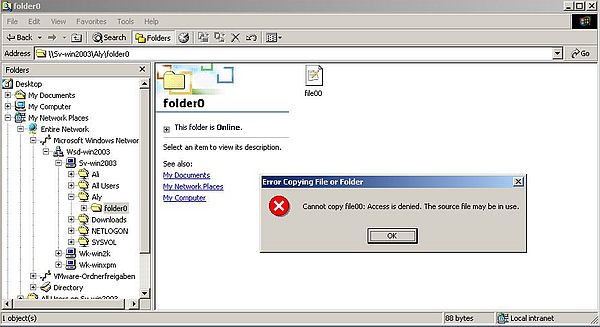
Now, let's enter the remote directory "folder0" and open the text file "file00.txt". This should work without any problem.
 |
We can modify this file's content in Notepad, but when trying to save it, we'll get the error message Cannot create the file. This is what we had to expect, as we configured the "Downloads" folder as read-only for all users.
 |
Saving the modified file to some local directory (such as "My Documents") is, of course, possible.
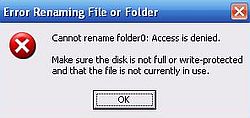
Copying the folder "folder0" to "My Documents" also works as it should. On the other hand, trying to rename or delete the folder will result in an Access denied error.
 |
The screenshots below show, how I modified the text file located in the "Aly" folder (screenshot on the left). Saving the file to that folder succeeds (remember, that "Aly" has full control of the files in the directory with his own files on the server). The screenshot on the right has been taken on Windows Server 2003, after "Aly" saved the file. The file content has well been modified.
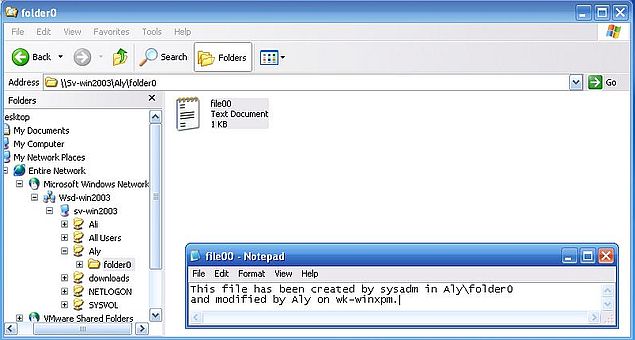 |
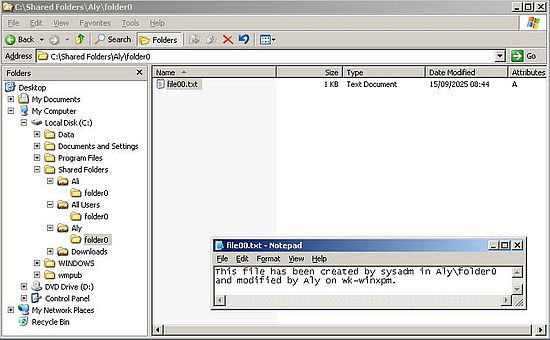 |
It is also possible for "Aly" to create a new file in the "Aly" directory (or one of its subdirectories) on the server. As well as deleting the files and folders, that have been created in this directory by the local Windows Server 2003 "Administrator" user.
"Aly" has full control over his own files, but has only read access to the files and folders in the directory "Ali" (these files belong to "Ali"). Trying, for example to copy/paste a file into that directory will result in an Access denied error.
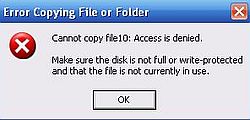 |
And finally, what happens when we try to access a remote file and folder, when Windows Server 2003 has meanwhile been shut down? Not possible to access the shared resource, of course; error message: The specified network name is no longer available.
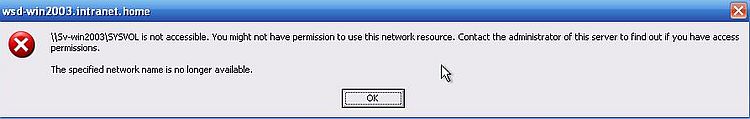 |
Accessing the shares from Windows 2000.
Open My Network Places > Entire Network. This opens a window with links to search Active Directory. Do not use these links. They result in the startup of the Microsoft Office 2000 Professional installer (?) and a difficult to close error message box, because the setup program cannot be found. Instead, use the link to view the entire contents of the network.
In the opening window, you'll find three items: Microsoft Windows Network, a VMware network in relationship with shared folders, and Directory. When opening Microsoft Windows Network, you'll find a network icon named Wsd-win2003; that's our Windows Server 2003 domain. View the Setting up Windows Server 2003: Client connection part of the tutorial, if you want to have a look at the screenshots of these network related windows.
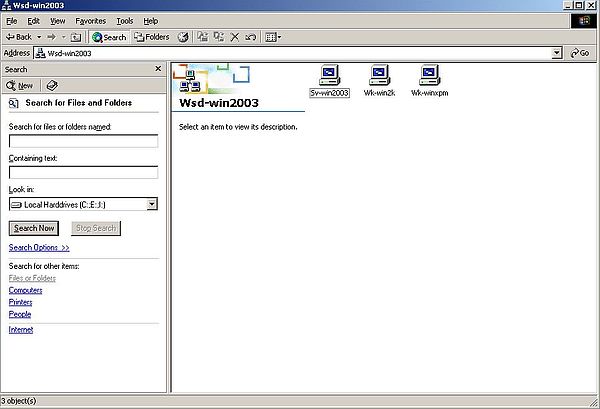
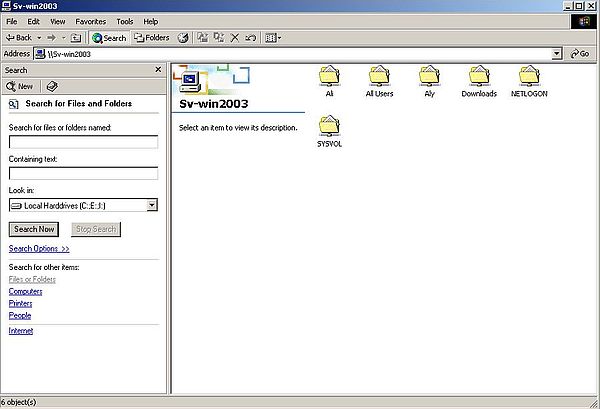
When you open Wsd-win2003, you'll find the server (Sv-win2003), the Windows 2000 computer itself (Wk-win2k), and (if it is actually running) the Windows XP computer (Wk-winxpm) (screenshot on the left). Double-clicking the server icon, opens a window, showing all shares on our Windows Server 2003: SYSVOL and NETLOGIN, available by default (I have not figured out, what these shares are for?), and the 4 custom folders that we configured to be shared (screenshot on the right).
 |
 |
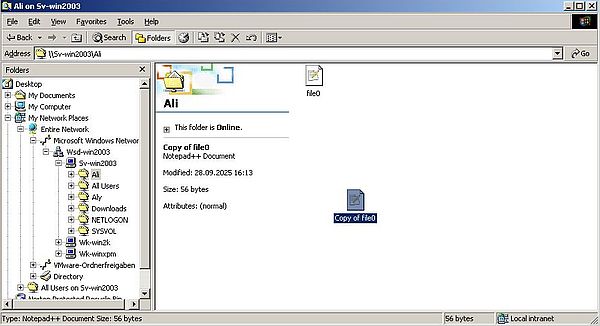
The screenshot below shows how "Ali" duplicates a file, originally created by user "Administrator" on Windows Server 2003, in his own folder on the server.
 |
As "Ali" has full control of his own files and folders, renaming the file created by "Administrator" is allowed, as well as deleting the two files in the "Ali" folder.
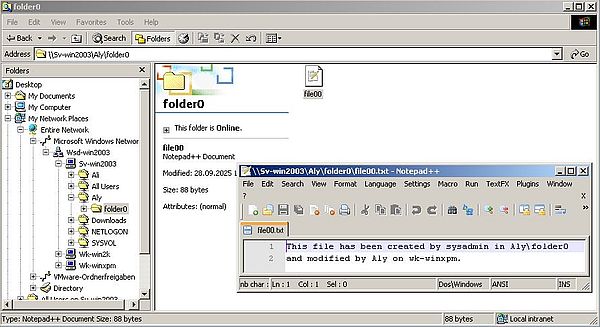
The screenshots below show user "Ali" accessing the files in the "Aly" folder. Opening a text file and viewing its content is allowed (screenshot on the left), whereas duplicating this file (i.e. writing to the "Aly" folder) results in an Access denied error (screenshot on the right).
 |
 |
Accessing the "All Users" folder.
When we configured the shares on the server, we set NTFS rights for the "All Users" folder such that all domain users may create and modify files, without however having the right to delete (or rename) them, except for user Admin, whom we gave full control. Let's now test if all this works as we want.
The screenshot shows how "Aly" tries to open "All Users" in the folder list, displayed in the Find Shared Folders window. Result: Display of an error message telling us that Windows cannot find \\sv-win2003\all_users.
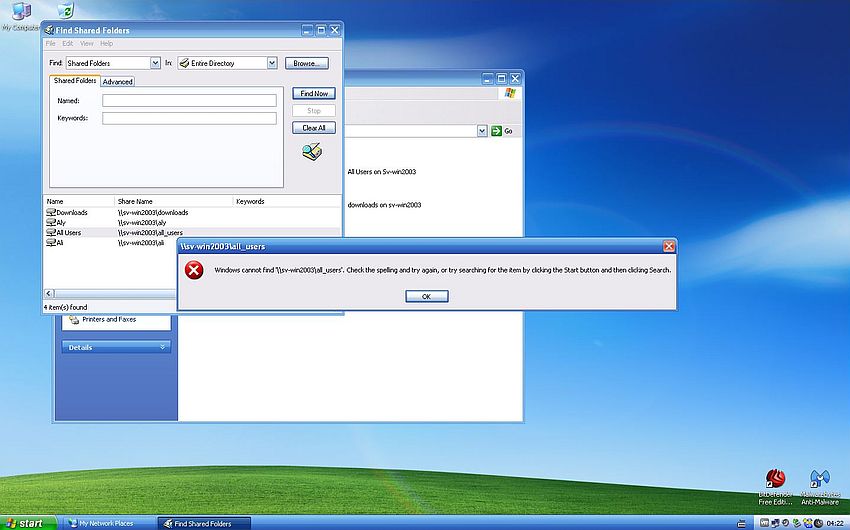 |
I suppose that the problem is the space in the name of the share (?). Another possibility is the fact that the share name ("All Users") is different from the folder name part of the network path ("all_users") (?).
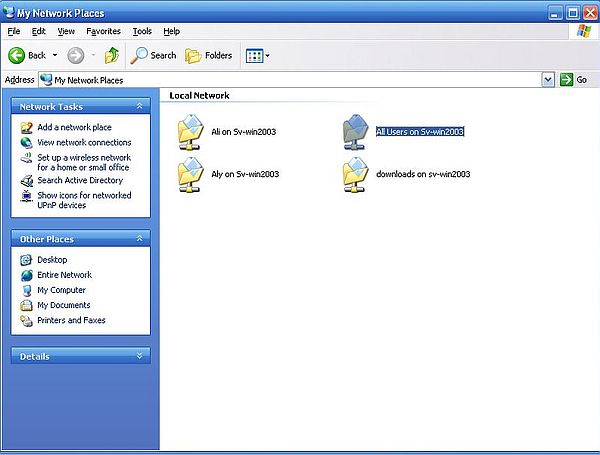
Anyway, the 4 shared folders are displayed in My Network Places (screenshot), and double-clicking the "All Users" folder here, opens it as it should. Another way to open it, is to proceed as we did above on Windows 2000.
 |
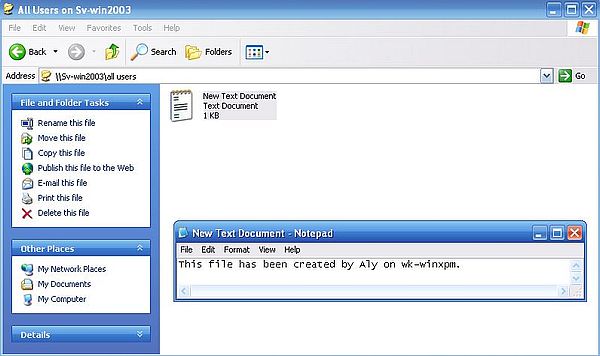
The screenshots below show user "Aly" (on wk-winxpm) creating a text document (screenshot on the left), and user "Ali" (on wk-win2k) modifying it (screenshot on the right).
 |
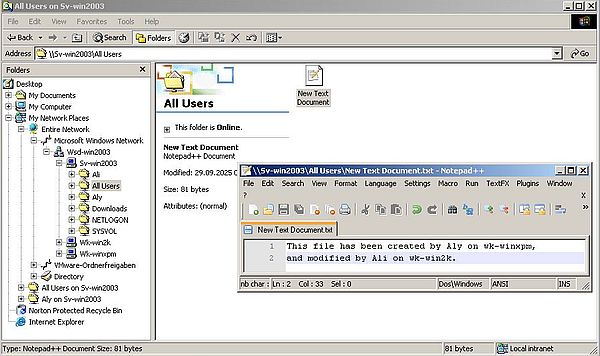 |
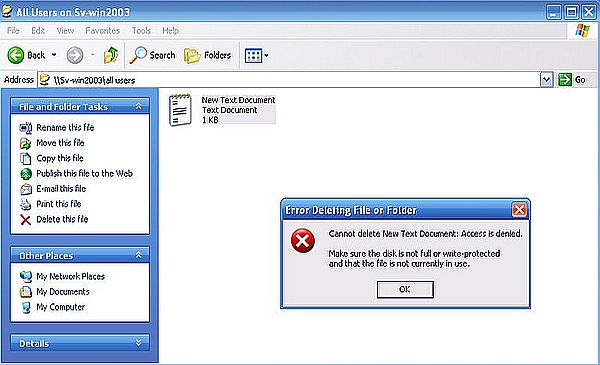
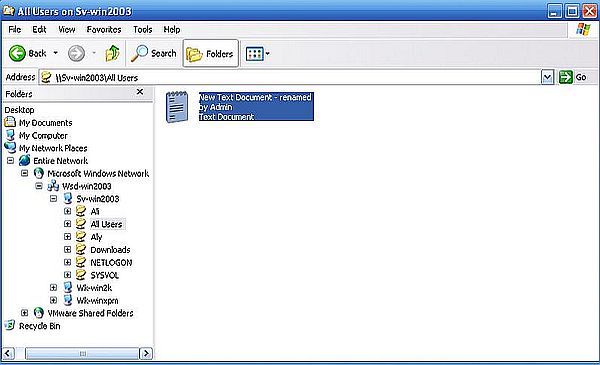
The screenshot on the left shows how user "Aly" fails to delete the text document in "All Users" (error message: Access denied). This is the case for trying to rename the document, too. The screenshot on the right shows how user "Admin" ("Aly" logged out, "Admin" logged in), who has full control of the "All Users" files and folders, succeeds to rename the file.
 |
 |
Network drives mapping.
For your convenience, you should map the shared folder to a disk drive. Doing so, the network drives will appear together with the local drives in the My Computer window of File Explorer, and you can directly access the shares.
To map a network drive in Windows XP, choose Tools > Map Network Drive... from the menu bar of File Explorer. The Map Network Drive dialog box opens. Enter a drive letter, and use the Browse button to navigate to the shared folder, that you want to map to this drive. The screenshot shows how I map the "Downloads" folder on sv-win2003 to the K: drive on wk-winxpm.
![Windows Server 2003: Accessing the shares from Windows XP - Network drive mapping [1] Windows Server 2003: Accessing the shares from Windows XP - Network drive mapping [1]](../screenshots/win2003_sharesaccess16.jpg) |
The folder has actually to be specified as a network path, in the case of the "Downloads" folder, this has to be \\Sv-win2003\Downloads. Before clicking the Finish button, be sure that the Reconnect at logon checkbox is selected.
![Windows Server 2003: Accessing the shares from Windows XP - Network drive mapping [2] Windows Server 2003: Accessing the shares from Windows XP - Network drive mapping [2]](../screenshots/win2003_sharesaccess17.jpg) |
Note: Mapping the "All Users" folder this way, results in the folder name \\Sv-win2003\All Users, without the underscore used when setting the network path on Windows Server 2003. The share is actually accessible this way. Does this mean that the failure to connect from the Find Shared Folders window is due to the fact that the name of the share is different from the folder part of the network path, rather than to the space in the folder name? To be sure to avoid problems, I would suggest to use folder names without spaces, and also to use the name of the share as folder part of the network path.
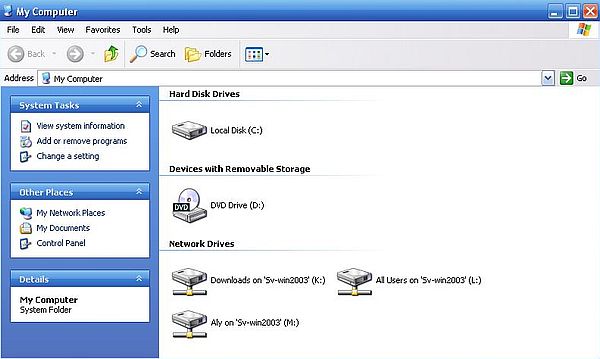
I mapped "All Users" to the L: drive, and the "Aly" folder to the M: drive. The screenshot below shows the network drives in File Explorer.
 |
The screenshot below shows the successful creation of a text file on drive L: (in the remote "All Users" folder).
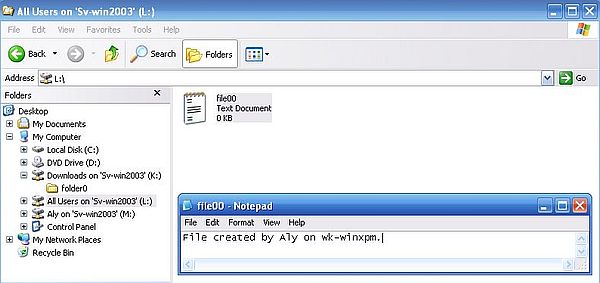 |
Mapping a network drive on Windows 2000 works exactly the same way as on Windows XP. The screenshot shows the mapping of the "Download" folders to the K: drive.
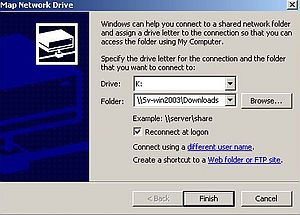 |
I mapped "All Users" to the L: drive, and the "Ali" folder to the M: drive. The screenshot shows the network drives in File Explorer.
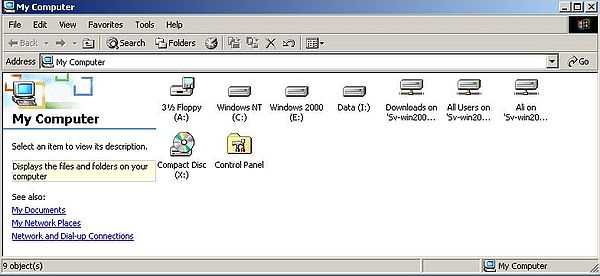 |
Note: If you wonder why my Windows 2000 is installed on the E: drive (that looks weird, doesn't it?), view my tutorial Installing a Windows 2000 and Windows NT dual boot
And to terminate part 6 of my Windows Server 2003 tutorial, here is a screenshot, that shows how "Ali" accesses the L: drive, and successfully modifies the text document, created by "Aly" in the remote "All Users" folder before.
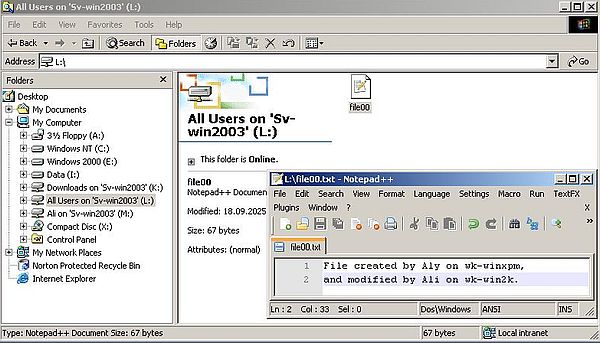 |
If you find this text helpful, please, support me and this website by signing my guestbook.